A capacitor is a
passive component, which stores electrical charge or electrical energy.
Capacitors are more commonly used components in an electronic
circuit. it is used for storing electrical energy. Capacitors vary by
their voltage, dielectric material, capacitance, tolerance etc.
Photo credit: g3npf.co.uk
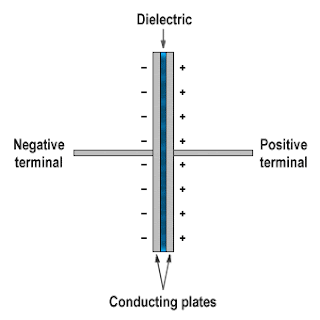
Structure of a Capacitor
The
capacitor consists of parallel conductive plates that do not touch
each other and are separated by a dielectric material. It has two
terminals, which are connected to the parallel conductive plates
inside the capacitor. The conductive plates of the capacitors are
separated with an insulating material, which is called the dielectric
medium. The conductors of the capacitor come in various shapes and
sizes depending on the voltage and the amount of charge it stores.
Dielectric of the capacitor also varies depending on the voltage,
capacitance, and frequency of operation. Examples of dielectric media
are glass, air, paper, vacuum, metal
oxide, polystyrene film, polyester film, mica, semiconductor etc. The
conductors and the dielectric medium is enclosed in the body of the
capacitor.
Photo credit: engineersgarage.com
Capacitance
is the ratio of electric charge stored on each conductor to the
potential difference between them. The capacitance of a capacitor
depends on the surface area of the conductors, the distance between
each plates of the capacitor, and the dielectric constant of the
material. The greater is the
capacitance when there is greater area of the conductors, closer
distance between the plates of the capacitor, and greater the
dielectric constant. The capacitance is measured in Farad, which has
the symbol (F). One Farad is the capacitance when 1 coulomb of
electrical charge is stored in the conductor on the application of 1
volt of potential difference.
The charge stored by the capacitor is denoted by
Q = CV
Where,
Q is the charge stored by the capacitor, C is the capacitance value of
the capacitor, and V is the voltage applied across the capacitor.
Normal
value of capacitance is smaller and it is measured in microfarad,
nanofarad, and picofarad. A 3-digit code is used to indicate the value
of the capacitor. The capacitance value is written in letters and
numbers and also just in numbers according to the manufacturers
description. Capacitors are also characterized by the voltage
specification. The maximum voltage is the voltage that can be applied
to a capacitor without breaking down the capacitor. It is usually
written on the capacitor along with the capacitor value.
Photo credit: engineersgarage.com
Operation of a Capacitor
A
capacitor is isolated when there is no electrical charge across the
conductors. In an isolated capacitor, the conductors hold equal and
opposite charges on the conductor surface. When a DC voltage is
applied to the terminals of a capacitor, the capacitor gets
charged. The current begins to flow across the terminals and an
electrostatic charge develops across the conductive plates of the
capacitor. Energy as electrons are stored in the electrostatic field
across the plates. The positive charge gets collected to one plate
and the negative charge to the other. As the charges get accumulated on
the plates there is current flowing
through the terminals into the capacitor. The capacitor continues to
charge until its voltage equalizes with the voltage that is applied.
When the capacitor is fully charged, the current flow is reduced and
becomes zero. The capacitor is discharged gradually
over time when the voltage source is removed. It can also be
discharged when the terminals are made to contact with each other. When
a higher charge is stored in the capacitor, it can give a spark while it is discharged.
Photo credit: technologyuk.net
The breakdown voltage is the voltage that can be given to a capacitor
which when exceeded will cause the dielectric to breakdown and become
a conductor. The dielectric breaks down and becomes a conductor
causing a large current to flow through the capacitor. It depends on
the capacitor and the voltage specification that is being used. The
failure can be a with an explosion with the capacitor exploding and
spreading the contents around. When
selecting a capacitor for use, the breakdown voltage rating must be
twice or thrice the value of the operating voltage. Some capacitors such
as the electrolytic capacitors show polarity that has +ive and -ive terminals. When connecting these capacitors the polarity needs to be correct, otherwise the capacitor might get damaged.
Capacitor Applications
Capacitors provide very large resistance to DC and small resistance for AC. Capacitors are used for a variety of applications such as blocking DC
and bypassing AC currents, store charge in a flash camera, filtering
the power supplies from ripples and spikes, resonant tuned circuits and
frequency tuning in radios, coupling
of stages, tone control in audio circuit, timing circuits, phase
alteration, stabilizing voltage and power flows etc. Applications such
as storing very high charges as required in a battery are being
gradually developed.
Photo credit: technologyuk.net
Types of Capacitors
There
are many different types of capacitors, based on the type of conductive
electrodes and the dielectric used in making them. There are 2 major
types of capacitors, fixed capacitors and variable capacitors.
1. Fixed capacitors
A.
Film capacitors such as paper capacitor, metalized paper capacitor,
glass capacitor, mica capacitor, silver mica capacitor, ceramic
capacitor, polyester capacitor, polystyrene capacitor, metalized
polyester capacitor, polycarbonate capacitor, polypropylene capacitor, Teflon capacitor, porcelain capacitor, etc.
B. Electrolytic capacitors such as aluminum electrolyte capacitor, tantalum electrolyte capacitor, etc.
2. Variable capacitors
The variable capacitors include air variable capacitor, polyester film capacitor, etc.
Electrolytic Capacitors
The
electrolytic capacitors have a positive and a negative electrode.
Aluminum is used as the electrode in an electrolytic capacitor. A thin
oxide layer act as the dielectric material in this capacitor. These
capacitors can vary in capacitance from 1 micro Farad to thousands of
micro Farads. It is used in varying DC voltage
conditions for power supply applications. Electrolytic capacitors are
used as ripple filters in power supply units and also as a filter
for bypassing low frequency signals in audio amplifiers etc. There
is polarity written on an electrolytic capacitor either + or - sign,
which indicates the terminals when connecting to the voltage.
Reversing the terminals of the electrolytic capacitor can cause
damage to the capacitor and also sometimes the capacitor may explode
with some gases and the contents inside.
Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum
capacitors are electrolytic capacitors and they use tantalum as the
electrode plates. They are superior than the aluminum electrolytic
capacitors in temperature and in frequency. They have high stability
and are used in circuits which demand high stability in capacitance
values. They are used in analog signal
circuits. It is a little bit more expensive than the electrolytic
capacitors. Tantalum capacitors comes in values such as 0.33 micro Farads, 0.47 micro Farads, 10 micro Farads etc.
Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are made of materials such as titanium and barium oxide used as the dielectric. They are usually seen as disc shaped. The capacitance values are considerably smaller. They have no polarity.
They are suitable for high frequencies. They are mostly used to bypass high frequency signals to the ground in circuits. Usual values of ceramic capacitors are 10 pico Farad, 100 pico Farad, 0.01 micro Farad, etc.
Polystyrene Film Capacitors
These
capacitors have the polystyrene film as the dielectric. Copper is used
as the electrode material They are used in filter circuits, and in
timing circuits.
Electric Double Layer Capacitors
These
capacitors are also called as super capacitors. Super capacitors
store large capacitance and have values in farads, which is a large
value of capacitance. They have values such as 0.47 Farad.
Polyester Film Capacitors
These
capacitors use polyester film as the dielectric material. They do not
have high tolerance level and have reasonable tolerance of +/-5 to
+/-10. They are very cheap. They comes in values ranging from 0.001
micro Farads, 0.1 micro Farads, 0.22 micro Farads etc.
Polypropylene Capacitors
Polypropylene film is used as the dielectric. These capacitors are used where higher tolerance is necessary.
Mica Capacitors
These
capacitors use Mica for the dielectric. Mica capacitors have good stability as their temperature coefficient is small. They have good insulation. They have high frequency tolerance and so they are used in resonant tuned circuits and high frequency filters etc. They also
have high voltage tolerance. Usual values for Mica capacitors are 47 pico Farads, 220 pico Farads, 1000 pico Farads, etc.
Metallized Polyester Film Capacitors
These
are a type of polyester film capacitor. Their electrodes are thin and
so they are small in size. They are rugged and they have no polarity.
Photo credit: electronics-made-easy.com
Variable Capacitors
Tuning Capacitors
This
is a large variable capacitor used for tuning the radio. It is also
called as a gang condenser. It consists of 2 sets of plates, which can
be varied by a spindle or a tuning control. There may be rotation
control, spindle, or screws that helps to vary
the capacitance. Air or polyester film is used as the dielectric. When
an air is used as a dielectric usual values that can be varied is 5 pico Farads to 40 pico Farads and in polyester film capacitor, 12 pico Farad
to 150 pico Farad can be varied.
Trimmer Capacitors
These
are capacitors, which can vary their capacitance values. The value of
the capacitance is varied by the use of a control. They have moving
plates fixed one above the other in sets. One set of plates can be moved
while the other set may be fixed to the frame. The movable plates are
rotated to vary the capacitance range. The
capacitor is varied by turning a screw. Mostly air or polyester film is
used as the dielectric. They are used in fine tuning and adjusting the
resonant circuits in a radio.





No comments:
Post a Comment