A direct conversion receiver is a type of radio receiver, which uses an unmodulated carrier frequency of the same frequency as that of the incoming radio frequency signal to mix using a synchronous detection technique and detects the audio or information from the received signal.
Here the unmodulated carrier frequency is generated by the local oscillator or the VFO. The local oscillator signal mixes with the incoming radio frequency signal and produces a beat note. The circuit is not so complex as compared to the superheterodyne receivers, but it lacks dynamic range. It can demodulate signals in modes such as CW, SSB and digital modes, but cannot detect signals in the AM or FM modes. Direct conversion receiver is also called the homodyne receiver, synchrodyne receiver or zero IF receiver.
Operation of a Direct Conversion Receiver
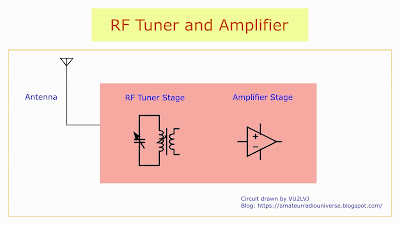
The signal from the antenna is tuned using a bandpass filter or a tuning circuit, which selectively tunes to the required frequency. A local oscillator signal is generated at the same frequency as that of the incoming radio frequency signal.
The incoming signal from the antenna is mixed with the local oscillator signal that is generated by the VFO in an RF mixer. The frequency of the local oscillator signal and the incoming radio frequency signal are the same. These two signals mix with each other in the mixer stage and are converted into a baseband audio signal.
The RF components are filtered using a low pass audio filter to produce only the audio frequency signal at the output. The modulated RF signal is converted directly to the baseband signal by a single conversion and therefore, it is called the direct conversion, homodyne or zero IF receiver.
The output audio signal is then amplified using an audio preamplifier and a power amplifier.
Advantages of DC Receivers
- A DC receiver does not have the complexity of the superheterodyne receivers such as multiple frequency conversions, multiple IF amplifier stages, image rejection problems etc.
- This receiver has high selectivity and therefore, it demodulates the signals quite precisely.
- It does not need a separate product detector stage.
Disadvantages of DC Receivers
Applications of DC Receiver
- Due to the lack of IF amplifier stages and automatic gain control, the baseband signal strength fluctuates over a wide range. This fluctuation of the baseband signal depends on the strength of the incoming signal.
- It demodulates CW, SSB and digital pulsed signals well, but is unable to detect AM or FM signals. It requires phase locking of the local oscillator to the incoming carrier signal, which is more difficult to achieve.
- A beat signal is always heard when trying to resolve AM signals in a DC receiver.
- There is an audible hum generated in some DC receiver designs.
Applications of DC Receiver
- With the development of IC chips incorporated with phase-locked loop circuits, the potential uses extends to demodulation of AM radio signals and other complex modulation techniques.
- Direct conversion receivers are used in receiver applications such as software defined radios, cellphones, television, medical imaging, avionics etc.






No comments:
Post a Comment